
TOPIC 5: QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS | CHEMISTRY FORM 4
Qualitative analysis involves determining metals and non metals (or metallic and non-metallic elements) present in a given sample. It is a process used to determine what elements (or radicals) are present in the sample.
identifying what (quality) substances are present in a sample.
Qualitative analysis may be divided into examination of:
- acidic or non-metallic radicals or negative ions;
- basic or metallic radicals, including ammonium ion.
The Importance of Qualitative Analysis in Real Life
contaminants in the environment. This may require the application of qualitative analysis procedures to identify the chemical composition of a given contaminant. Qualitative analysis methods are highly employed by environmental scientists to detect and identify different contaminants in the environment.
Determination of ions present in a chemical substance
the characteristics of the solution formed serve as a clue to establish
the type of elements present in a tested sample. The mixture formed
following dissolution of a solid sample may be a clear solution, an
emulsion or a precipitate. The solution or emulsion is further analysed
to detect the ions present in it. The precipitate is then separated from
the filtrate and both are subjected to further tests to identify the
kind of elements present.
the products of the reaction. In some cases, the smell of the gas may
not suffice to detect the gas, especially if the gas is colourless and
odourless. In such cases, the gas is subjected to various qualitative
analysis tests in order to establish its identify.
The nature of a chemical substance such as its solubility in water,
characteristic smell, flame colour, and the characteristics of its
reaction products can be used to identify the chemical substance under
test. In this way, the nature and identity of unknown substance can ultimately be known.
SOIL ANALYSIS
Determination of soil pH
certain types of indicators. This procedure is purely qualitative
because it involves observation of the change in colour of indicators to
determine the pH of the soil. For further details on the measurement of
soil pH, read a topic on Soil Chemistry (Chapter Three) in this book.
particular soil. Such tests include test for nitrate, sulphate, chloride
and phosphate ions. Determination of soil composition gives soil
scientists information necessary for conservation.
Qualitative analysis techniques are applied in medical field, for example in
carrying out various tests such as testing blood and urine samples,
determining the level of blood sugar, pregnancy diagnose and blood
grouping. Most of these analytical tests are done to diagnose a wide
range of diseases and medical conditions.
in detecting the causative agents for typhoid (salmonella typhi), the
blood is left to clot, or it is centrifuged in order to separate blood
corpuscles from plasma. The plasma is then subjected to various
qualitative tests to detect the presence of salmonella typhi.
in pregnancy diagnosis, a certain chemical is added to urine, where a
specific change in colour of the urine confirms whether one is pregnant
or not.
Qualitative analysis is also applied in blood grouping, whereby antibodies are
added to the blood to determine the blood group. Agglutination of the
blood corpuscles when antibodies are added help detect the group of the
blood.
Forensic scientists may use qualitative chemical analysis to identify substances
left at crime scenes, which can be vital in convicting criminals.
Application in industries
and make quality products.In chemical industries, the products often get
contaminated by unknown contaminants. Qualitative tests are done to
detect the contaminants. This may be followed by quantitative analysis
aiming at finding out the quantity (amount) of the contaminant present.
tests. Just a small error can cause misinterpretation of the contents of
a tested sample. The following are few but important measures that
should be observed when carrying out qualitative analysis experiments.
After adding the test reagent, make sure the solution is stirred thoroughly.
Before making any inference, wait until the solution has completely
settled down. Often, additional quantities of the reagent must then be
added so that an excess is present.
Avoid contamination
Contamination of the sample or reagent should strictly be avoided. For instance, if
the contaminant contains a cation, the test can give misleading positive
results. To avoid contamination of the sample and apparatus, the following precautions should be observed:
All the apparatus should be cleaned and dried thoroughly and must remain clean throughout the experiment.
Do not lay a glass rod on a dirt laboratory bench as it can get contaminated easily.
Avoid touching the side of a test-tube with the tip of a dropper. The contaminant can be picked up and transferred to another solution, a fact that would contaminate the solution, thus producing false results.
Only distilled water from the wash bottle should be used to dissolve the solids. Spring, rain or tap water contains chemicals that can lead to wrong results and conclusions.
Warming up the solution
beaker of warm or boiling water (water bath). The test-tube is kept in a
water bath for some time, with constant stirring. Then, the solution is
tested for the presence of anions or cations contained in it.
pouring a drop of the solution to be tested on it. The colour of the
paper is observed and noted while the paper is wet. Once dry, the colour
may change or disappear, resulting in wrong interpretation.
Qualitative Analysis Procedures
The procedures of qualitative analysis involve carrying out analytical
tests in the appropriate sequence of steps. The common procedures for
testing an unknown sample is to make its solution and then test this
solution for different ions present. The steps involved in the systemic
analysis of a given sample are as follows:
- Colour and smell
- Flame test
- Solubility in water
- Dry heating
- Action on litmus (for gases evolved)
- Dilute acid test (dilute H2SO4)
- Concentrated acid test (concentrated H2SO4)
- Wet test for acid radicals
Preliminary Test on an Unknown Sample
Preliminary tests include noting the appearance (colour, texture, feel, etc) of the
sample, detecting the smell of the gas liberated, observing the action
of a substance on litmus, and even the taste of the substance under
investigation. The preliminary tests give a clue about the type of the elements present in a sample.)
| Gas | Colour | Smell | Action on litmus | Test |
| CH3COOH | Colourless | Vinegar-like | Acidic | Liberated as dense white fumes |
| N2 | Colourless | Odourless | Neutral | No chemical test |
| Water vapour | Colourless | Odourless | Neutral | Turns white CuSO4 blue |
| NO2 | Reddish-brown | Pungent | Acidic | Not as red as Br2 vapour and does not condense on the sides of the test tube |
| NH3 | Colourless | Pungent | Alkaline | Forms thick white fumes when in contact with HCl gas |
| HCl | White fumes | Irritating | Acidic | Forms thick white fumes when in contact with NH3 gas |
| HBr & Br2 | White fumes & reddish- brown gas | Choking | Acidic & bleaches | HBr resembles HCl, & Br2, condenses to a red liquid on the sides of the test tube |
| Cl2 | Pale green | Bleaches | Choking | Gives white fumes with NH4OH |
| I2 | Violet | Choking | Bleaches | Turns starch iodide paper blue-black |
| CO2 | Colourless | Odourless | Slightly acidic | Turns lime water milky |
| CO | Colourless | Odourless | Neutral | Burns with pale blue flame |
| H2 | Colourless | Odourless | Neutral | Burns with a „pop‟ sound |
| H2S | Colourless | Rotten eggs | Acidic | Burns with blue flame to SO2, blackens lead acetate paper. |
| O2 | Colourless | Odourless | Neutral | Re-ignites a glowing splint |
| SO2 | Colourless | Irritating smell of burning sulphur | Acidic | Decolourizes KMnO4 solution, turns K2Cr2O7 from orange to green |
| SO3 | Colourless | Pungent | Acidic | Fumes in moist air forming dense white fumes |
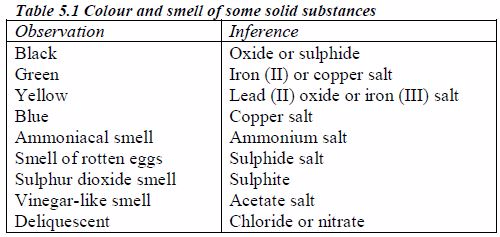
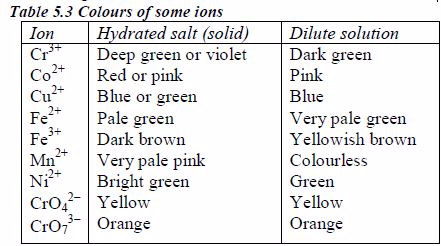
Colours of some ions in solution
The appearance of a substance in solid or solution form can help in its identification:
If a compound and its solution in water are colourless, it is probable that a transition metal is absent.
If its colour is black, it is probably an oxide or a sulphide.
If the solid and its solution in water are coloured, probably a transition metal is present.
Preparation of Stock Solutions from Soluble and Insoluble Salts
different compounds
To test the solubility of a compound,
put one spatula of the compound in 1cm3 of distilled water and stir. If
the compound is soluble, this
amount will dissolve. If the compound is moderately soluble, some of
this amount will dissolve. If the compound is insoluble, not even a
small amount will dissolve.
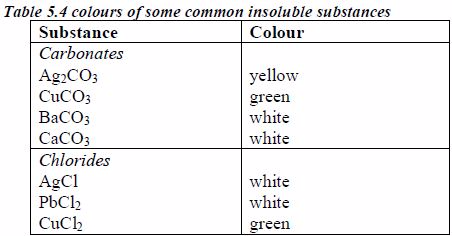
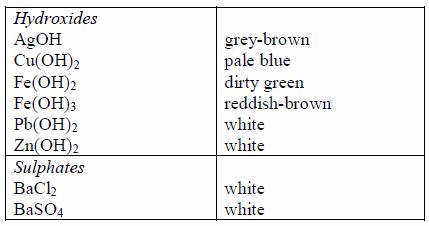
The following are some general rules on the solubility of different compounds in water:
All common nitrates of metals are soluble.
All common sodium, potassium and ammonium salts are soluble.
All common chlorides are soluble except those of silver, mercury (I) and lead (II).
All common sulphates are soluble except those of lead and barium. The sulphates of calcium and silver are sparingly soluble.
All carbonates, sulphites and phosphates of sodium, potassium, and ammonium are soluble but other common carbonates are insoluble.
Sodium, potassium and ammonium hydroxides [(ammonia solution, NH3(aq)]* are soluble but other common hydroxides are insoluble.
All sulphides are insoluble except those of the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals and ammonium.
solution of ammonia in water (ammonia solution) is always wrongly termed
as ammonium hydroxide. Although the name ammonium hydroxide suggests an
alkali with the formula [NH4+][OH–], it is actually impossible to
isolate samples of NH4+ and OH– ions from a solution of ammonia in water
since the ions are negligibly very few in solution except in extremely
dilute solutions.
Different substances decompose on heating to give different products. Many
compounds decompose on heating and leave solid residues. In performing
this test, the compound is heated in an ignition tube or dry test tube.
Heating is continued until no further change occurs. The gas evolved,
residue left or sublimate formed on heating may help to identify the
acid radical present in a compound.
Table 5.5 Action of heat on the test substance
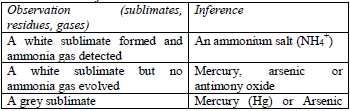
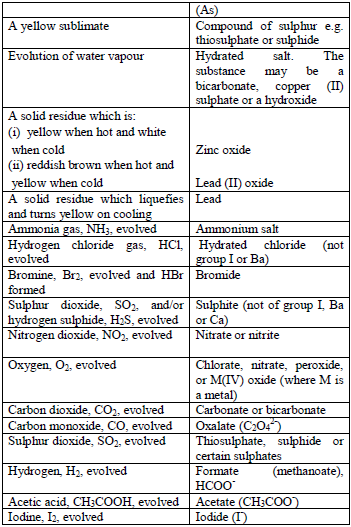
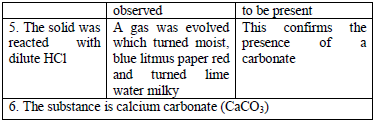
Treat the solid with cold dilute sulphuric or hydrochloric acid. Identify the
gas evolved. If there is no reaction with the cold acid, heat the
mixture gently. Heat carefully and ensure the mixture does not boil. The
gas evolved can be identified as follows:
Table 5.6 Detection of acidic radicals

As in the above test, the acid is added to the solid substance and if no
reaction occurs, the mixture is warmed gently, but the mixture should
not be boiled. Then, the gas given off is identified. In addition,
observe any product, other than the gas, which results from the reaction.
Table 5.7 Action of conc. H2SO4
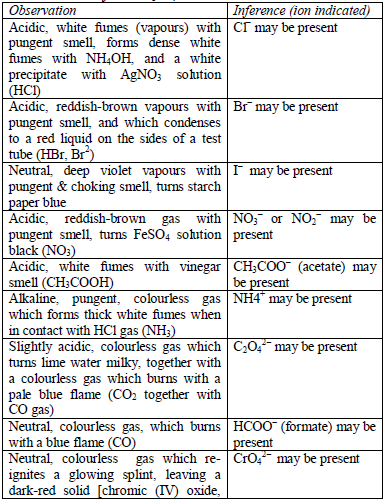

Note:
Oxalates give CO2 with concentrated H2SO4 but not with. HCl.
Nitrates do not give NO2 when treated with HCl but nitrites give NO2 gas.
If no result is obtained in the above tests, the salt is probably a sulphate, chromate or phosphate.
Precipitation of Insoluble Salts from their Solutions
Precipitate insoluble salts from their solutions
The detection of acidic radicals is important in that, in addition to other
information, it enables a clear-cut identification of the substance
being analysed. The substances are first dissolved in distilled water to
make solutions. Then, the resulting solutions are tested for radicals.
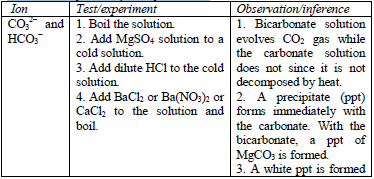
Table 5.8 shows a list of test/experiments, each of which confirms the presence of a given ion. Depending on the availability of reagents, students can do any of the listed tests to confirm the ions present in test solutions.
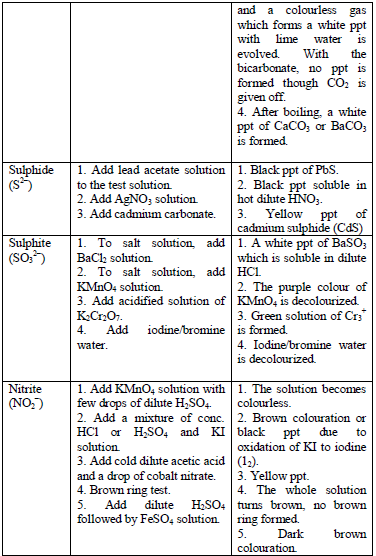
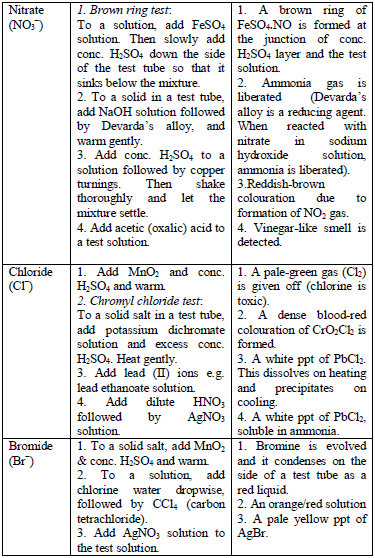
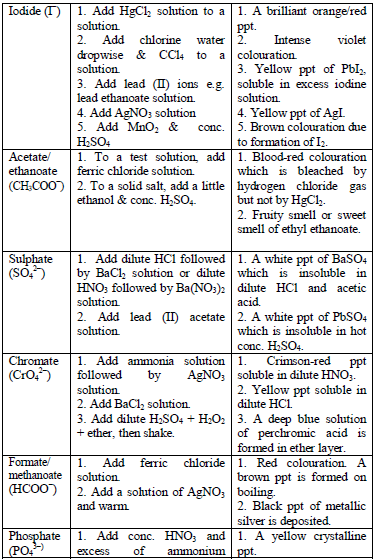
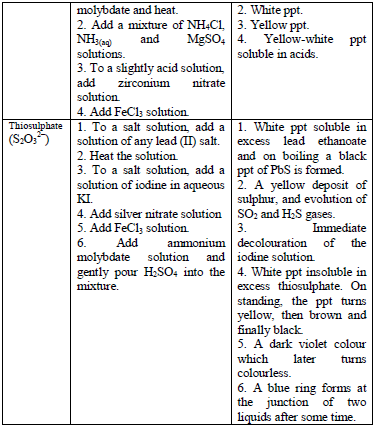
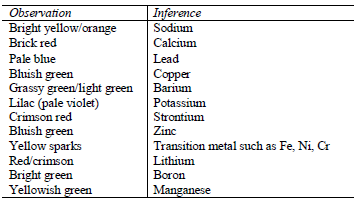
Flame test
Some metal ions can be identified by the colour of their flame during a
flame test. Flame test involves mixing solutions of ions with conc. HCl
and then heating them on a platinum or nichrome wire over a non luminous
flame. Alternatively, a dry solid can be used instead of the
solution.To perform this experiment, dip a platinum or nichrome wire
into concentrated hydrochloric acid and hold it just above the blue part
of the flame. Repeat the process until the wire is clean. After that
dip the clean wire into the acid and the dip it into the solution of the
test substance (or its solid particles). Heat the substance strongly
and observe the colour of the flame formed.
Add dilute hydrochloric acid dropwise to the test solution until the
solution tests acidic to litmus paper. Observe for any reaction. A
precipitate will form with any cation that forms an insoluble chloride.
For example:
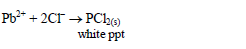
Action of sulphuric acid
Add dilute sulphuric acid dropwise to
the test solution until the solution is acidic. Observe for any
reaction. A precipitate will form with any
cation that forms an insoluble sulphate. For example:

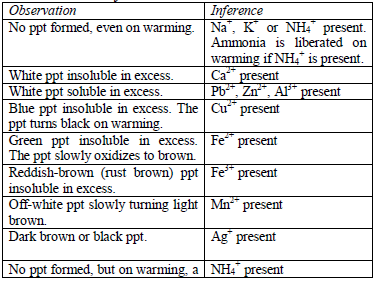
Add sodium hydroxide solution, a little at a time, to the test solution
until there is an excess of it. Stir or shake the mixture and observe
for any reaction. If no precipitate is formed, warm the mixture gently
and test for ammonia. If a precipitate forms, continue adding the sodium
hydroxide solution.
Table 5.9 Reaction of cations with dilute NaOH

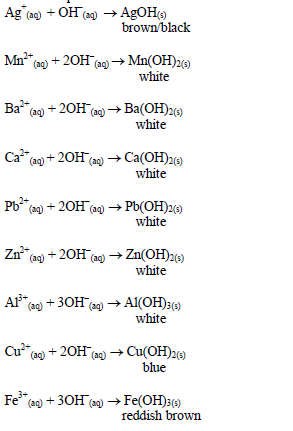
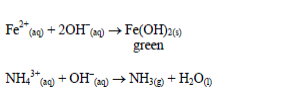
hydroxide. This is due to the amphoteric nature of the hydroxides of
these metals.

Action of aqueous ammonia
shake the mixture and observe for any reaction. If a ppt forms, continue adding aqueous ammonia.
Table 5.10 Reaction of cations with aqueous ammonia
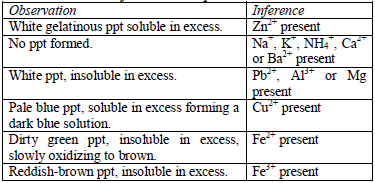

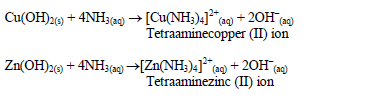
Confirmatory tests for cations
carry out confirmatory tests to confirm the presence of cations in substances.
Table 5.11 Confirmatory tests for cations
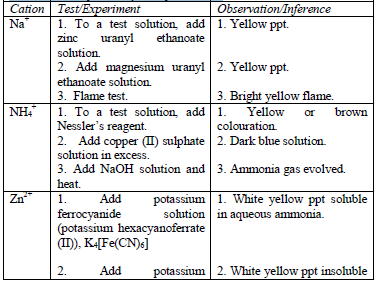
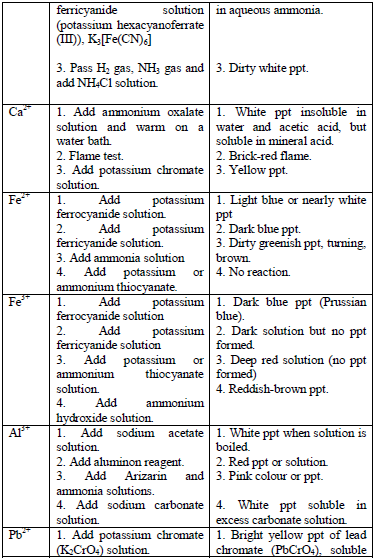
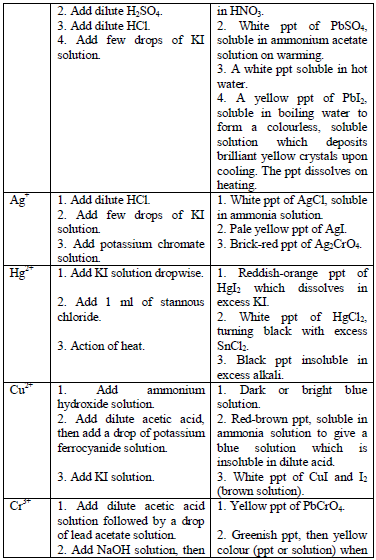
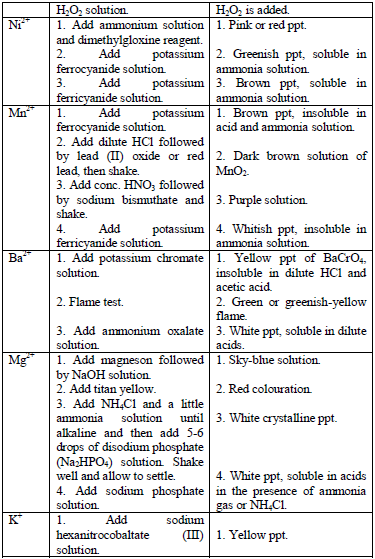

Confirmatory tests for iron salts
The original test solution has to be divided into three portions. Then the solutions should be treated with the following reagents and the results recorded as shown in table 5.12.
Potassium hexacyanoferrate (II) solution
Potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) solution
Potassium thiocyanate solution
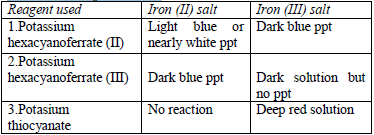
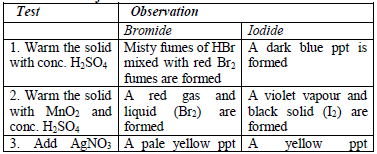
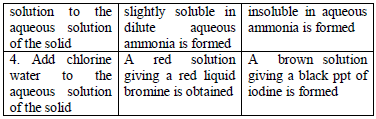
All the observations made and any experimental data obtained during the
experiment (or test) must be presented in a tabular form a shown below.
Results presented in a table are concise, easy to read and understand.
The last column of the table gives the conclusions based on the
observations made.

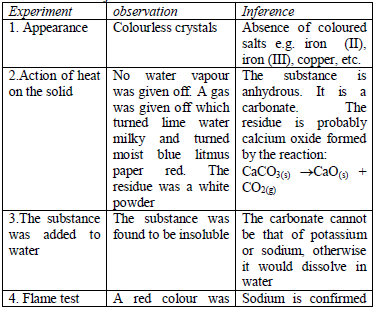

No comments:
Post a Comment