
GOVERNMENT OF TANZANIA
Government
Meaning and Types of Government
Explain the meaning and types of government
The government is asystem or organizational machinery for organizing people. In other words, government is a group of people within a community who have power and authority to perform administrative functions. These includeplanning, making decisions and even the implementation of policies. Government can be created through elections, by force or through hereditary means. The government manages relations between people and their institutions or organizations
Types of governments
The criteria used to categorize governments isbased on how a given government has acquired its position,themeans of formation of the government and the power distribution among the three organs of the state. The most appropriate way of categorizing governments is based on how government leaders get into power. This refers toapeaceful election process or violent processes used to acquire government power. Based onthese criteria, there are only two major types of government; democratic governments and non- democratic governments
Democratic Government
A Democratic Government is aform of government whose political power is determined by popular vote. This type of government takes into consideration the consent of people in decision making, which means it acquires legitimacy from the people through free and fair elections. A good example of a democratic government is the presidential system of government in USA. On the other hand, in a Parliamentary system of government, which is sometimes known as Westminster modal system, there is a separation of power between the head of government (who is selectedfrom the elected members of parliament) and the head of state. A good example of this government is the government of the United Kingdom. In that type of government, the head of government is the prime minister who is an elected member of parliament, while in the presidential system the head of state and government is the elected president. The president can form the cabinet by appointing ministers outside the legislature. United republic of Tanzania uses both the presidential and parliamentary system of government. In Tanzania, the president is the head of state, head of government and commander in chief who comes into power through the general election.
Non-Democratic government
A non-democratic government is the form of government which normally does not come into power by popular election. It is the government which gets into power without majority will and people’s legitimacy. In most cases a non-democratic government results from military coup due to the interest of some leaders. They tend to manipulate election process by imposing dictatorship styles. In this kind of government, only one person or a small group of people take control of the government. These are people who normally have great influence due to economic or social influence. A good example of a non-democratic government is the dictatorship governments like that of Adolf Hitler of Germany and Mussolini of Italy. Other examples are those of Democtratic Republic of Congo (DRC) formerly Zaire under Mobutu Seseseko and Uganda under Idd Amin Dada. The basic feature of all non-democratic government is the absence of democratic principles.
Dominant Forms of Government in the World are:
1. Republican government
This is a form of government in which a country is governed by a president and other politicians who are elected by the people. In this form of government more power is concentrated to a single person; the president. A good example of this government is that of the United Republic of Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, Democtratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and South Africa.
2. Union Government
This form of government is usually formed when two or more nations are joined together. Each nation surrenders its power and sovereignty to aunitary government. For example, the United Republic of Tanzania was formed when Tanganyika united with Zanzibar. The United Kingdom is the union of England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
3.Monarchical government (a monarchy)
This is a system of government whereby a king or queen rules the country. A king or queen comes into power by inheritance. Examples of monarchies are found in Swaziland, Morocco, the United Kingdom and Netherlands.
There are two types of monarchies.These are:
- Absolute monarchy. In this type of monarchy, a king or queen is the head of state and government. He or she forms the government and exercises power without being bound by rules. Swaziland is an example of a country which has an absolute monarchy.
- Constitutional monarchy. In this form of monarchy the king or queen is only the head of state. The prime minister is the head of government. The prime minister is elected by citizens in a general election. After being elected, he or she forms a government. Some of the countries with constitutional monarchies include Sweden, Japan, Jordan, The United Kingdom (UK) and Netherlands.
4. Federation
In this form of government, power is divided and shared between a national government and state governments. Member states have control over their own affairs but a central government controls national affairs. Examples of federal governments are: the Russian Federation, Nigeria and the USA.
5. Dictatorships
A dictatorship is a form of government whereby the leadership rests in the hands of an individual or a group of persons who come into power mainly through force. Dictators have unlimited authority over the people.
6. Communist Government
It is a form of government in a communist country, in which the government owns the major means of production including land. The government provides people with free health care, education and social welfare. A Communist government always results from socialist revolutions. A good example of communist government is North Korea and China.
7. Transitional Government
This is the form of government which is created temporarily by the people within a country while waiting for general government or permanent government. This happens when there is sudden change of government or leadership due to political instability in the country. However this form of government is not a formal system.
Importance of Government
Illustrate the importance of government
The followings are the importance of Government
- It provides citizens with social services like health care, education and safe water
- The government constructs and maintains infrastructure like roads, school buildings and hospitals.
- Maintenance of peace and order in the country is also the role of the government. The government provides security for citizens and their property through the police and the army
- Governments initiate and maintain relationships with other countries. The government leaders visit different countries and send ambassadors to those states. Other countries are also invited to do the same in Tanzania. Our country is a member of different international organizations including the United Nations, African Union and the Commonwealth.
- The government collects revenue for the development of the country. Citizens pay taxes to the government which, in turn, provides social services using the money collected.
- It guides the country by preparing and implementing good policies.
- Individual rights of citizens are protected by the government.
The Constitution
The constitution is the system of laws and basic principles that a country or an organization is governed by. The national constitution is the basic law of a country. This means that all other laws must conform to the provisions of the constitution.
Meaning and the Structure of the National Constitution
Explain the meaning and the structure of the national constitution
The constitution provides the framework of the country and creates the principle organs of the state as well as their powers and limitations.
Types of constitution
There are two main types of constitution: namely written constitution and unwritten constitution. The written constitution is the one in which basic principles are written down in a form of legal document. Many countries have adopted this type of constitution. For example, Tanzania, Kenya and USA. It acts as standard of reference to which government activities reflects upon. Also it minimizes chance of misinterpretation. Unwritten constitution is the one in which basic principles are not written in a single document, but they rely on various documents and other points of reference. A good example is Britain, where its constitution is based on statutes, customary and precedents and convectional practices.
How the Constitution is Made, its Importance, its Relationship to the Government of Tanzania, and How it is Safeguarded
Explain how the constitution is made, its importance, its relationship to the government of Tanzania, how it is safeguarded
The constitution of the United Republic of Tanzania of 1977 is divided into ten chapters. Each chapter is divided into several parts.
The following is the structure of our constitution.
Chapter one
This chapter has the following three parts:
1. The United Republic and the people. This part talks about the:
- Proclamation of the United Republic of Tanzania.
- Territory of the United Republic of Tanzania, which consists of the whole area of Tanzania mainland, Zanzibar, and territorial waters.
- Declaration of a multi-party state. Tanzania is a democratic and socialist state which follows multi-party democracy.
- Exercising of state authority. All Tanzania state authorities exercise their power under the control of six organs, which are:
- The Government of the United Republic of Tanzania.
- The Revolution Government of Zanzibar.
- The Judiciary of the United Republic of Tanzania.
- The Judiciary of Zanzibar.
- The Parliament of the United Republic of Tanzania.
- The House of Representatives of Zanzibar.
e. The franchise: This is the formal permission given to Tanzanian citizens aged eighteen and above to vote in any public election held in Tanzania.
2. Fundamental objectives and directive principles of state policy. This part describes:
- The interpretation of the government: According to the Constitution, the government includes the government of the United Republic of Tanzania, the Revolutionary Government of Zanzibar, local government authorities and any person who exercises power or authority on behalf of the government.
- The application of the provisions of this part of the Constitution: According to the constitution, this part is not enforceable by any court.
- The government and the people: The government derives its power and authority from the people through the Constitution.
- The pursuit of Ujamaa and self-reliance: Tanzania is a state that follows Ujamaa and self-reliance.
- The right to work, to educational and other pursuits: The Constitution recognizes every person’s right to work, to education and social welfare in times of sickness, disability or old age.
3. Basic rights and duties of citizens. This part explains:
- The equality of human beings: The Constitution recognizes that all persons are born free and equal and that every person is entitled to recognition and respect.
- Equality before the law: All people are equal and should be treated equally before the law.
- The right to life: All people have the right to live and be protected by the society.
- The right to freedom of conscience: Every person has freedom to live as a free person.
- The right to privacy and personal security: Every person has the right toprivacy, respect and protection of himself, his family and his properties.
- Duties to the society: Among other duties the citizens are supposed to participate in work, abide by laws, safeguard public property and defend the nation.
- General provisions on: (i) Fundamental rights and duties: The Constitution guarantees fundamental human rights for all persons in Tanzania. (ii) Limitations of basic rights, freedoms and duties: The Constitution limits individual rights and freedoms for the interest of other persons or the public.
- The extraordinary powers of the state authority about:(i) Derogation from rights and freedoms: The Constitution gives parliament the mandate to enact laws that will enable measures to be taken during a state of emergency or against persons who can endanger the security of the nation. (ii) Power to proclaim a state of emergency: The President has the power to proclaim a state of emergency when there is danger or war in the country.
Chapter two
This chapter has three parts which deal with the executive arm of the United Republic of Tanzania.
- The President: This part describes how the President is elected, the qualifications for election as President, the provisions for being re-elected and duties and powers of the President of the United Republic of Tanzania. It also describes the Government of Tanzania.
- The Vice-President: This is the principal assistant to the President. This part describes the qualifications and duties of the Vice-President.
- The Prime Minister, the Cabinet and the government
(a) The Prime Minister is appointed by the President but the National Assembly must approve him or her through a majority vote.
(b) Cabinet is made up of the Vice-President, the President of Zanzibar, the Prime Minister and all cabinet ministers. The ministers are appointed by the President after consulting the Prime Minister. There are also deputy ministers who are appointed by the President.
This part also points out the length of the ministers’ and deputy ministers’ terms of office. In addition, this part includes the Attorney-General, who is appointed by the President. The Attorney-General is the advisory of the government of Tanzania on legal matters. The secretary to the Cabinet and regional commissioners are also mentioned, and their duties explained.
Chapter three
This chapter describes the parliament. The parliament is made up of the President and the National Assembly. This chapter has three parts:
- Establishment of the National Assembly, its authorities, powers and its lifetime.
- Members, constituencies and election of members. This part explains who the members of the National Assembly are and how they are elected or appointed.
- Procedures, powers and privileges of Parliament. This part also describes the functions of the Speaker and Deputy Speaker and the procedures for electing them.
Chapter four
This chapter has the following three parts:
- The Revolutionary Government of Zanzibar and the President of Zanzibar: In this part the Constitution describes the head of the Zanzibar Government, his
- Authority and how he is elected.
- The Zanzibar Revolutionary Council: This part describes the members of the council, who are the President of Zanzibar as chairman, the Chief Minister, all ministers of the Zanzibar Government and other members appointed by the chairman.
- The House of Representatives of Zanzibar: Zanzibar’s House of Representatives comprises two parts. These are:
- The Head of the Revolutionary Government of Zanzibar who is also the President of Zanzibar.
- Members of the House elected or appointed according to the Zanzibar Constitution. These members are called Representatives. -
This part also explains the authority of the Representatives. Among their functions are.
- To question any ministry concerning public affairs in Zanzibar.
- To debate the performance of any ministry of Zanzibar.
- To authorize any plan intended to be implemented in Zanzibar.
Chapter five
This chapter deals with the judiciary. The judiciary refers to the country’s courts and court officials. Chapter five has seven parts which are:
- The High Court of the United Republic.
- The appointment of judiciary personnel by the Judiciary Service Commission.
- The High Court of Zanzibar.
- The Court of Appeal of the United Republic.
- Process of the courts.
- The special Constitutional Court.
Chapter six
This chapter has two parts:
- The Permanent Commission of Enquiry: The members of this commission are appointed by the President.
- The Public Leaders’ Ethics Secretariat, whose main task is to investigate the conduct of public leaders,
Chapter seven
Chapter seven deals with the finances of the United Republic in the areas of contribution and allocation of revenue. It also discusses the consolidated fund and the conditions for withdrawal of the money, the expenditure and other matters concerning union funds.
Chapter eight
This chapter deals with the establishment and functions of local government authorities such as municipal councils and county councils.
Chapter nine
It contains provisions on the armed forces and also describes the powers of the commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The armed forces are made up of the army, the navy and the air force.
Chapter ten
This chapter has miscellaneous (various) provisions. The areas dealt with include:
- Resignation of personnel from various offices.
- Procedure of succession in government offices.
- Interpretation of terms in the Constitution.
- Title, commencement and application of the Constitution.
- Union matters.
Activity 1
Which chapter in the constitution gives you different rights as a citizen? List then explain four rights described in that chapter
Making the constitution
The Tanzanian Constitution has not always been as it is contently. It has undergone several major changes since the first one was written in 1961. The following are the versions of the Constitution that Tanzania has had.
1. The Independence Constitution of 1961
Tanganyika got her independence from Britain in 1961. The British wrote a Constitution for Tanganyika which was used when Mwalimu J. K. Nyerere was the Prime Minister. This constitution is known as the Independence Constitution of 1961
2. The Republican Constitution of 1962
In 1962, the government of Tanganyika published a white paper proposing to make the country a republic. The National Assembly discussed the paper and adopted it. The National Assembly then passed an Act of Parliament to give it a legal right to be a Constituent Assembly. This Constituent Assembly discussed and adopted a new Constitution and Mwalimu J.K. Nyerere was elected the first president of the Republic of Tanganyika. This Constitution is known as the Republic Constitution of 1962.
3.The Interim Constitution of the United Republic of Tanganyika and Zanzibar of 1964
After the union of Tanganyika and Zanzibar there was a need to change the Constitution. So the President of Tanzania issued an interim constitutional decree which modified the Constitution of the Republic of Tanganyika. The new Constitution was the Interim Constitution of the United Republic of Tanganyika and Zanzibar of 1964.
4.The Interim Constitution of Tanzania of 1965
In 1965, the Parliament of the United Republic of Tanzania enacted an Act of Parliament to make the Interim Constitution of Tanzania. This constitution declared Tanzania a single party state. Tanganyika African National Union (TANU) of Tanzania mainland and Afro-Shiraz Party (ASP) of Zanzibar were the only political parties recognized by the Constitution. This Constitution was the starting point in uniting TANU and ASP so that Tanzania could become a real-one party state. This Constitution is known as the Interim Constitution of Tanzania of 1965.
5.The Constitution of the United Republic of Tanzania of 1977
In 1977, TANU and ASP united to form Chama Cha Mapinduzi (CCM). This union created the need for a new Constitution. The then president of Tanzania Mwalimu J.K. Nyerere appointed a Constitutional Commission of twenty people to oversee the making of a new constitution. Each side of the union was represented by ten members.
President Nyerere appointed the representatives of the Constituent Assembly to consider the proposal of the Constitutional Commission to enact the constitution. The members of the Constituent Assembly were 45 from Zanzibar and 156 from Tanzania mainland. They discussed and agreed on the constitutional proposals made by the Constitutional Commission, then, the current constitution was adopted. This constitution is known as the Constitution of the United Republic of Tanzania of 1977.
Constitutional amendment
Constitutional amendment is the process of improving or changing the laws in the constitution for the aim of improving the laws in the constitution.
The 1977 Constitution has many amendments. These amendments were made to cater for the changing needs of the society. The major amendments are:
- The introduction of a Bill of Rights in the Constitution in 1984.
- An amendment to introduce the multi-party system in Tanzania in 1992.
- In 1995, another amendment introduced the Vice-President as the President’s running mate in the elections. It also made the president of Zanzibar a member of the Union Cabinet.
The changes made are;
- It changed the mode of electing the President. Previously, the President was elected by majority vote. This amendment allowed the President to be elected by the highest votes.
- It increased the number of seats allocated to women in Parliament to thirty percent.
- The independence of the judiciary and its powers on legal matters were established.
- It established the Human Rights and Good Governance Commission.
Importance of a national Constitution
The Constitution is very important to the country for the following reasons.
- The Constitution protects the rights of individuals.
- It ensures that the government is fair and just to its citizens.
- The Constitution establishes the main organs of the state. These are the Executive, the Judiciary and the Legislature.
- It describes the form of government that is used in the country.
- The Constitution gives guidance on how disputes between the organs of the state are to be resolved.
- It defines the limits of the power of leaders.
- It shows how leaders are to be chosen.
Relationship between the Constitution and the Government of Tanzania
Generally, the relationship between the Constitution and the government is that the Constitution guides the government on all matters of leadership.
- The Constitution defines the form of government to be used in our country.
- It is the Constitution that establishes the organs of the state and outlines their powers.
- The government has to be based on principles of democracy, human rights, social justice and observance of sovereignty of the state as the Constitution prescribes.
- The leaders of Tanzania at all levels are elected as per the Constitution. Those who are elected lead according to the Constitution’s guidelines.
- The Constitution states the terms of the leaders in the offices.
- The elected leaders take an oath to defend the Constitution.
Ways of protecting the constitution
Since the Constitution is the law of the land, it must be protected by every member of the society. There are different ways of protecting the Constitution of our country. The following are some of them.
- The existing Constitution was made by a body which dissolved after finishing its task. This makes the Constitution supreme since there is no one above it.
- All laws of the country are derived from the Constitution and no one can make laws which contradict the Constitution.
- The courts of law protect the Constitution by ensuring that all people are allowed to enjoy their rights.
- The government and non-governmental organizations educate the society so that they can understand and protect their constitutional rights.
- Mass media educate people about their rights so that when these rights are abused, they can demand them at the courts of law.
Exercise 1
A. Use the words in the box below to answer the questions that follow.
| Government, Republic, Federation, Union, Dictatorship, Monarchy, Constitution |
- A form of government whereby power is divided and shard between a national and state government is called ______________________
- The group of people and institutions responsible for controlling a country or state is called_________________
- A form of government whereby two or more countries unite to form a single state is called ___________
- A form of government in whereby the leadership rests in the hands of an individual or a group of persons who come to power through force is called __________
- The system of principles that a country is governed by is called_________
- A system of government whereby a king or queen rules the country is called____________
- A form of government whereby a country is governed by a president and politicians elected by the people are called ____________
Exercise 2
B. Write ‘T’ for true statements and ‘F’ for false statements.
- One importance of a government is to provide social services to the citizens.
- The Constitution of the United Republic of Tanzania is divided into seven chapters.
- Chapter two of the Tanzania Constitution describes the parliament.
- The Independence Constitution of 1961 was made by the British colonialists.
- The current Constitution of 1977 was made by the President.
C. Match the statements in list A with those in list B.
| LIST A | LIST B |
|
|
- Write three reasons why the national Constitution is important.
- Give two relationships between the Constitution and the government.
- Mention two ways of protecting the constitution
Local Government
In order for the government to run its functions effectively, it needs to involve people in their respective areas. Village governments, wards, divisions, district, urban and region constitute the local authorities (government). So local government represents people in their grass-root level. Without effective local governments, no democracy can be natured. Local governments are total governments and are important, working hand in hand with the central government.
Meaning of Local Government
Define local government
Local governments are the governments which are formed at the grass- root level in order to assist the central government in matters of administration and other important activities. These governments have powers over, districts, cities and municipals or urban areas. They are created to perform administrative activities at the local levels. The members of these authorities are elected by the residents of these areas. The local government authorities were established in 1982.
Reasons for the establishment of local government
To give more power to the people in the localities. This enables people to participate in government work, plan the development of their areas and maintain peace and order in their areas.
To widen the system of democratic leadership. In their localities, people are able to elect and be elected. This ensures peace and harmony and therefore fulfills the local people’s social, economic and cultural aspirations.
Structure of Local Government
Describe the structure of local government
There are two categories of local government authorities, these are: rural authorities, which are also known as district councils, and urban authorities. The district councils range from the village level to the district level.
The urban authorities are responsible for the administration and development of township, municipalities and cities.
District authorities
1.The village government
This is the smallest unit of a local government. The following is the structure of the village government.It’s formed by 250 house hold. Any area with the number of people mentioned above qualified to be village government. Also the minister who is responsible for local government may declare two units of the same to form a single village, depending on the size and nature of the units which they wanted to unite. Village government works through its major organs which are village assembly and village council.
(a)The village assembly
It is composed of the entire adult population living in the village. The head of the assembly is the village chairperson who is elected by the village assembly. The following are some of the functions of the village assembly:
- Adopting by-laws of the village.
- Electing the village chairperson.
- Electing the village council.
(b)The village committees
There are different committees in the village, including planning, finance, economic affairs, social services, security, forest production and water resources. The committees perform different roles in the village according to their specialized categories.
(c)The village council
Members of the village council are twenty-five in number;they are elected by the village assembly. Their head is the village chairperson. The village council is the executive arm of the village assembly. It performs the day-to-day governance activities of the village under the supervision of the Village Executive Officer (VEO) who is appointed by the district council.
The following are some of the functions of the village council:
- Planning and coordinating village activities.
- Giving assistance and advising the villagers on developmental matters like agriculture and industry.
- Encouraging village residents to undertake and participate in communal enterprises.
- Proposing by-laws for the village.
2. The ward government
The ward government is composed of the following:
(a) The ward development council
This is the highest organ in the ward. It is comprised of:
- (i) The chairperson, who is the ward councilor. The ward councilor is elected by the people who live in that ward. He or she runs the office for a period of five years, and may be re-elected. The councilor represents the ward in the district development council.
- (ii) Chairpersons of all village councils within the ward.
- (iii) The members of the district council who live in the ward.
- (iv) Civic groups involved in the promotion of development in the ward, for example, non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
Some of the roles and functions of the ward development council include:
- (i) Developing general plans for the ward.
- (ii) Managing disasters and other environment-related activities within the ward.
- (iii) Reviewing the proposals for the village councils’ projects and passing them on for further approval at the district level.
(b)Ward executive officer
The ward executive officer supervises all developmental activities in the ward. He or she is appointed and employed by the district council.
(c)Ward departments
There are different departments in the ward, including:
- (i) Department of social welfare.
- (ii) Department of health.
- (iii) Department of education.
- (iv) Department of agriculture and livestock.
- (v) Department of finance.
3. The district councils
The district council is composed of:
- Elected members from each ward in a district.
- Members of parliament from constituencies within the district.
- Three members appointed by the Minister for Local Government Authorities.
- One member representing the village councils.
The District Executive Director (DED) is appointed by the President. He or she is the secretary to the district council.
The district council has the following committees:
- District Development committees.
- Finance, administration and planning committee.
- Economic, construction and environment committee.
- Education, health and water committee.
- Ethics committee.
The roles and functions of district councils
- Supervising the implementation of all plans for economic, commercial, industrial and social development in the district.
- Approving by-laws made by the village councils.
- Coordinating plans, projects and programmers for the villages in the district.
- Providing environmental protection and management in the district.
- Promoting the social welfare and economic well-being of residents.
- Passing by-laws applicable in the district.
- Submitting by-laws to the regional officer for comments and re-submitting the by-laws to the Minister for Local Government Authorities for approval.
Urban authorities
Urban authorities include town councils, municipal councils and city councils.
1. Town councils
Examples of town councils in Tanzania are Bukoba, Lindi and Songea. A town council is composed of:
- Members elected from the wards within the town.
- Members of Parliament who represent the constituencies within the town.
- Three members appointed by the Minister for Local Government Authorities.
Each town council has a town director who is the chief executive.
2. Municipal councils
These are found in towns with a population of over 80,000 residents. Tanzanian municipal councils include Dodoma, Morogoro, Kinondoni, Ilala and Temeke.
A municipal council is composed of:
- Members elected from the ward within the municipality.
- Members of Parliament who represent the constituencies within the municipality.
- Three members appointed by the Minister for Local Government Authorities.
Officials in municipalities are:
- The mayor, who is the head of the municipal council and is assisted by the deputy mayor.The two are elected from among councilors.
- A municipal executive director.He or she is a secretary to the municipal council.
- The chairperson and vice-chairperson of the municipality.
3. City councils
Tanzania currently has five cities, namely Dar es Salaam, Mwanza, Arusha, Tanga and Mbeya. The city council is composed of:
- Councilors, one from each ward in the city.
- Members representing constituencies in the city.
- Members of Parliament representing constituencies within the city.
- Six members appointed by the Minister for Local Government Authorities from among the city residents.
Officials in the city council are:
- The mayor. He or she is the head of the city council and is assisted by the deputy mayor. A mayor is elected from among the councilors and stays in office for five years. They may be re-elected.
- The city director. He or she is the chief executive, and is appointed by the President. He or she is also a secretary to the city council. Urban authorities have committees.
The following are some of them.
- Economic affairs, health and education.
- Urban planning and environment.
- Finance and administration.
The roles of urban authorities include:
- Facilitating the maintenance of peace, order and good governance.
- Promoting social welfare and the economic well-being of the local community.
- Furthering social and economic development of their areas.
- Taking necessary measures to suppress crime and protect public and private properties.
- Regulating and improving agriculture, trade, commerce and industry.
- Enhancing the health, education, social well-being and recreational life of the people.
- Eradicating poverty.
The following are the general functions of urban authorities:
- Taking and requiring the taking of measures for conservation of natural resources, prevention of soil erosion and prohibition of improper cultivation.
- Inspecting all foodstuffs and liquids intended for human consumption and seizing and destroying the foodstuffs or liquids which are unfit for human consumption.
- Keeping the environment clean.
- Taking measures aimed at preventing injury to public health.
Activity 2
Give the names of the following leaders in your area then describe their importance to the society.
- Ward councilor.
- Member of Parliament for your constituency.
Functions of Local Government
Identify functions of local government
The establishment of local government at the district and urban areas aimed at performing various functions to the people in their specific localities. Local government can perform those functions as directives from the central government. According to the Tanzania constitution, the following are the functions of local governments:
- It performs the functions of local government within its area
- It ensures enforcement of law and public safety
- It consolidates democracy within its areas
- It solves the problems facing the local people within a particular area
The functions of local government are divided into two main groups which are: Mandatory functions and permissive functions.
Mandatory functions are those functions performed by local governments as directives from the central government. These functions are assigned by the large country frame work, and are performed according to the national laws, which include:
- The maintenance of law and order
- Promotion of social and economic welfare, and wellbeing of all people within the area
- To collect and make proper utilization of revenue
- To make by-laws for the materials and local policies
- To make advancement of social and economic development in accordance with material policy and plans.
- To make consideration, regulation and coordination of projects and plans
Permissive functions are those functions which the local government may perform depending on the nature of the area, the need and availability of resources, particularly the fiscal resources. These may include:
- Building, equipping and letting of shops and houses
- Establishment.maintenance, operating and control of damage and sewage works
- Building and maintaining health centers and primary schools
- Charging fees for services and licences
Participating Actively in Function of either School or Local Government
Participate actively in function of either school or local government
Among the aims of establishing the local government is to bring about social and economic development in each specific area by involving people from grass-root. To fulfill this, each one ought to participate in performing various responsibilities, such as working in the community in support of particular cause; paying required taxes. Licences and other duties; attending political and community meetings and monitoring and criticizing local government activities that might against the law such as corruption and embezzlement of public fund.
Why the Local Government has an Important Effect on One's Life
Explain why the local government has an important effect on his/her life
The functions of local government have positive effects on people’s lives. These effects are: -
- Peace, order and harmony prevail in their localities.
- Production is conducted without any interference. The peaceful environment allows people to participate effectively in economic activities.
- There is freedom of expression and freedom of participation in decision-making on matters affecting the society.
- Local governments encourage democratic participation. Councilors are elected after every five years. The residents of each area are free to participate fully in electing their councilors. Thus, people elect the leaders that they want and remove incompetent leaders through elections.
- People benefit from what they contribute to the local government. Residents pay taxes and in turn get services such as education, garbage collection and health facilities.
- People are kept informed about the policies of their local government authorities. As a result, better decisions are made in the local areas.Sources of local government revenue
Sources of Local Government Revenue
Explain sources of local government revenue
Revenue is also called income. The following are the main sources of revenue for local government authorities.
Sources of Revenue
1. Rent
Examples of rent are:
- House rent from council houses.
- Rent from market stalls.
- Land rent and service charges.
2. Licenses
A licence is a permit from an authority to carry out an activity, own or use something. A person can apply for a licence for things such as:
- Auctioning
- Retail trading
- Fishing
- Driving
- Entertainment
3. Duties
Duties are fees paid for certain goods and services. Examples include:
- Customs duties, paid on goods brought into the country.
- Stamp duty, paid for some legal documents.
- Excise duties, paid for some goods made, sold or used within the country.
4. Contributions
Residents living in an area contribute to their local authority through:
- Fees under by-laws.
- Court fines.
- Paying for the use of community centers.
- Holding fund raisers for community projects.
5. Grants and loans
These are funds given by the central government and various local and international agencies to the local government authorities.
How the Local Government spend its Revenue
Explain how the local government spends its revenue
Expenditure is the act of spending or using money.
The local government authorities spend money in the following ways:
- Salaries, wages and allowances paid to the local authority officials and employees.
- Operational costs, for instance telephone, water and electricity bills.
- Maintenance of assets, e.g. painting council houses and updating computer software.
- Paying consolidated fund services, constitutional offices and debts.
- Development expenditure for instance road construction and maintenance, building schools and clinics.
Control of local governments
Local government falls are under the Prime Minister’s office where there is a ministry responsible for local government and regional administration.
The Regional Commissioner is the assistant proper officer for the district councils, town councils and village councils established within his or her district.
The Minister for Local Government Authorities and the Regional Commissioners are empowered to approve the annual budgets of their respective authorities. In the district, town, municipal and city councils, there are directors. These directors are accountable for the councils’ funds.
Central Government
The central government is the government which deals with matters concerning the whole nation.
Meaning of Central Government
Explain the meaning of central government
This kind of authority is called central government because all the power over the country are centered on them. To exercise its power the central government has different organs which perform different duties. Ministries and directorates are examples of supporting tools of the central government.
The Structure of the Central Government
Describe the structure of the central government
According to the constitution of the United Republic of Tanzania, the central government of Tanzania is made up of the executive, the parliament and the judiciary. These organs have been separated so as to: work cooperatively and facilitate the principle of checks and balance within the state; eliminate corruption, serve the people; enhance efficiency and smooth operation of the government; promote transparency and accountability; facilitate division of labour and make coordination and administration easily.
Figure; The structure of the central government
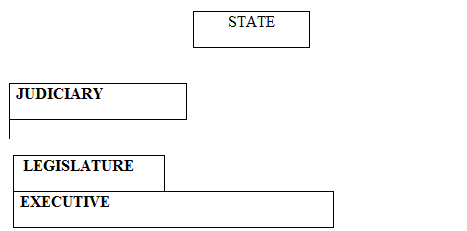
Functions of the Central Government
Explain the functions of the central government
The function of the central government can be viewed through the joint work of the three organs of the state which are executive, legislature and judiciary.
Difference between Local and Central Government
Differentiate between local and central government
Local government can be differentiated from local government as follows:
- The authority of local government is exercised at the villages, wards, district, town, cities and municipal level while central government has authority to control the whole country.
- Central government makes by laws for the aim of controlling a small unit while central government makes laws which govern the whole country.
- In local government there is greater chance for citizens to participate directly in decision making due to the small population compared to the large area the central government covers. Direct participation by every person is not possible in the central government.
- Local governments are made up of village councils, district councils, town councils, municipal and city councils while the central government is made of the president, vice president, cabinet and the prime minister.
- The administration in the central government is simple to operate its activities faster because of the size while central government involves a large area and administration is difficult.
- Local governments are servants of central government; since the central government provides orders to the local government, as the local governments acts as subordinate of the central government.
Sources of Central Government Revenue
Identify sources of central government revenue
There are several sources of income in the country. Among these are:
- Direct tax- The main form of income tax is direct tax, which is paid by all governmental and private sector employees. It includes monthly payments, interest on investments and profit from other governmental business.
- Indirect tax- This includes import and export duties which are known as custom duties. Are good example of indirect tax is the value added tax (vat) which was introduced in Tanzania in 1998.
- Domestic loan borrowing: An example of domestic loan borrowing is the sale of government bonds and treasury bills to the public. The government also borrows money from external sources such as foreign governments and institutions, like IMF, World Back and African Development Bank (ADB).
- Grants: These are external sources of the central government revenue. They are non-payable funds. They are just provided to poor countries as a free assistance.
- Charges from provision of the government services: The governments obtain revenue by charging users of the social public services provided to them like water, electricity and medical treatments. The government has established the policy of cost sharing in order to ensure that revenue is realized.
- Licenses: These are documents which validate property ownership or someone’s competences. For that case, a person who wants to conduct any business must pay for it. Also licenses, such as, driving licenses validate drivers competences. Driving licenses are normally after every three years.
- Profit from estates and public co-operations: The government fully owns some estates or co-operations while in others, the government the majority shares. As the result of these, the government receives large shares of the profit made. For example the government gets profit from TANESCO, NMB, Sisal and Tea estates, just to mention a few.
- There are other sources such as industries, tourism sectors, agriculture sectors and others which bring foreign currency to the nation.
Central Government Expenditure
Explain the central government expenditure
The revenue collected by the central government is used in different ways in order to enhance development of the society.
- It is used in promoting social services such as Education and Health services. For example, the government uses a lot of money in building schools and hospitals in different parts of the country.
- The government uses its fund in the process of improving transport systems such as construction of roads. These process make the government pat companies which are involved in the construction and the materials needed in the construction process.
- Other funds are used to help disadvantaged groups such as orphans, widows, refugees, the disabled and the aged.
- The government uses its fund to buy different needs, such as, stationery materials like pens, pencils and exercise books for people and students in schools.
- Also the government uses its income to pay internal and external debts.
- The government uses its revenue to pay workers salaries and other charges like leaves, on transit and housing.
- In agricultural sector, farmers are provided subsides to help them improve its farming activities.Political parties which have parliamentary seats in the national assembly and counselors in local councils are also given subsides.
Participating in different Central Government activities
Participate in different central government activities
Activity 3
Participate in different central government activities
The Reasons for and Importance of Tanganyika and Zanzibar Union
Tanganyika and Zanzibar united in 26th April, 1964. This led to the formation of The United Republic of Tanzania. The article of the union was ratified by the Act of 1964 of the parliament of Tanzania, called the Union of Tanganyika and Zanzibar Act of 1964.
The Reasons for and Importance of Tanganyika and Zanzibar Union
Explain the reasons for and importance of Tanganyika and Zanzibar union
The reasons of the Union Tanganyika and Zanzibar
- People of Tanganyika and Zanzibar experience similar culture and historical experience. They had similar culture aspects such as Kiswahili language, dancing and building styles. They were involved in similar economic activities, For example trade before and after colonialism. Both African states suffered and experienced similar problems of colonial domination.
- Security and defense to protect these two countries from being invaded by external enemies. The nature and location these two countries could create conducive environmental for enemies to destruct peace and security.
- To consolidate cooperation and integration of people who lives in these two countries.
- To avoid expansion of capitalism into Zanzibar. This is because capitalism was a threat to these two socialist countries, and the two were forced to join.
- The spirit of Africanism was another threat for the union. The proponents of the union were influenced by Pan- Africanism. One among of the important goals of Pan Africanism was unity for all Africans. In the name of fulfilling this goal, it led to the Union between Tanganyika and Zanzibar.
Importance of the Union between Tanganyika and Zanzibar
- To facilitate free movement of people from one part of the Union to another, especially after removing the carrying of passport. This increases the contact of the people between the two parts hence consolidating their brotherhood. To enhance cooperation in economic activities. People from any part of the union can conduct trading activities freely. The union expands the market for the goods produced in the region.
- To distribute the wealth due to existing natural resources: Each part has been benefiting from natural resources existing in any part of the nation. For example, hydro-electric power produced in the mainland benefit both sides of the nation.
- Identity of African countries’ unity possibility. The union of Tanganyika and Zanzibar is good example that can be considered uniting Africa. It shows success in fulfilling the dreams and desire of black people. The Union has succeeding in creating strong Army and other state instruments which have responsibility to maintaine peace, defense and security.
Union Matters in the Government of United Republic of Tanzania
Identity union matters in the government of the United Republic of Tanzania
After the formation of the Union, there were matters referred to as union matters. These matters are twenty two as shown below.
- The constitution and the government of the united republic of Tanzania
- Foreign affairs and international cooperation (external affairs)
- Defense and security
- Police force
- Power to declare a state of emergency
- Citizenship
- Immigration
- External trade and borrowing
- Public services for united republic
- Income tax, Customs and excise duties
- Harbours, air craft, posts and telegrams
- Financial matters, legal tenders and currency
- Industrial licenses
- Higher education
- Mineral resources, including petroleum and natural gas
- National examination council and all matters relating to the council
- Aviation and air transport
- Research
- Meteorological matters
- Statistics
- Court of appeal of the United Republic
- Registration of political parties and other matters relating to political parties.
Non-Union matters
These are matters looked after by specific government apart from the union government. These include all matters which are not mentioned above. Among of the non-union matters are:
- Local government matters
- Road maintenance and travel
- Agriculture, livestock, fisheries and other means of livelihood
- Trade and small scale industries
- Prison
Challenges of the Union
Although the union between Tanganyika and Zanzibar has existed for long, there are some challenges facing the union. For example, commodities bought in Zanzibar are taxed in Tanzania main land. This is because custom duties in Zanzibar are considered to be less compared to that of mainland. Some politicians demand for the presence of three governments- Tanganyika, Zanzibar and the Union government while others want to remain with only one government of The United Republic of Tanzania.
Strategies for Improving the Union's Stability
Suggest strategies for improving the union's stability
In order to strengthen the union, different strategies should be employed for the welfare of the entire nation in Tanzania. The following are some of the strategies which would enhance the unity between Tanganyika and Zanzibar.
- We should consolidate cooperation in cultural affairs such as sports and games by introducing the union cup. There should be encouragement in trade between the people of Tanzania main land and Zanzibar
- Free movement of people within the member countries must be ensured. This will make people to feel that they are together in the same country and consider themselves as relatives.
- The presence of a ministry in the president’s office to deal with the union should maintain fairness and justice. Leaders of the both sides of the union should frequently and seriously meet and discuss different issues regarding the central government.
Exercise 3
A. Use the words in the box below to answer the questions that follow.
| duties, ward, government, cities, peace |
- The system in which local authorities are in charge of the administration of districts and urban centers is called local --------------
- District authorities are made up of the ‘village government, _______ and the district councils.
- Urban authorities are in charge of towns and ___________
- One of the functions of local government is maintaining ________________order.
- Local governments get revenue by charging ___________
Exercise 4
B. Write “T” for the true statements and ‘F for false statements.
- Local authorities ensure peace and order in their areas.
- Students can participate in the functions of local government by planting trees.
- Ward governments are made up of village governments and district councils.
- Building schools is part of the development expenditure of local government authorities.
- The city director is appointed b) the district council.
Exercise 5
C. Match the statements in Column A with those in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
|
|
- READ TOPIC 3: Democracy



No comments:
Post a Comment